
- ADD LAYER ARCMAP HOW TO
- ADD LAYER ARCMAP DOWNLOAD
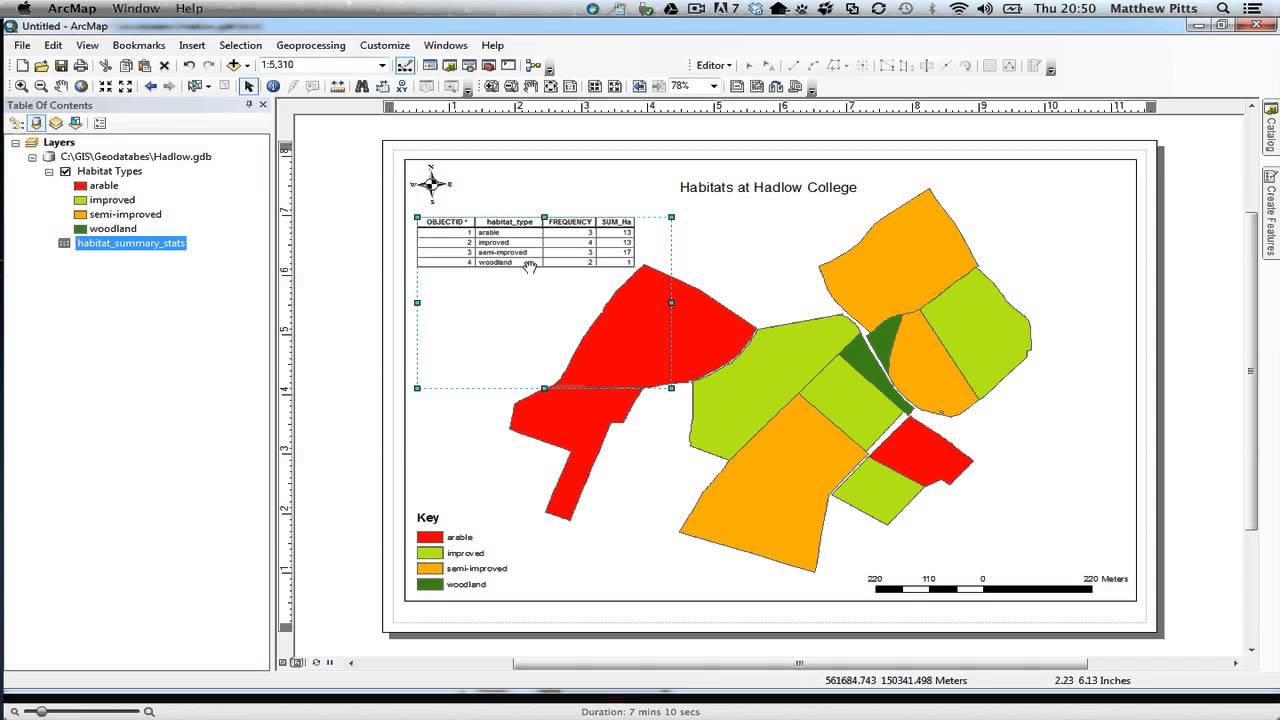
Navigate to ArcGIS_Lesson3\Scans and select the ErosionMap1954a.tif raster image, then click the Add buttonĪ dialog window appears where ArcMap will ask if you want to create PyramidsĪrcMap will then inform you that the spatial reference to this file is unknown (the purpose of this lesson is to add spatial reference to the raster image). The next step is to add the scanned images that you are going to georeference. Click the toolbar by its name, slowly drag it above the map display, then drop it. You may wish to anchor the toolbar to the ArcMap window (or leave it floating, as you prefer). Click Customize > Toolbars > Georeferencing to display the toolbar. You must add the appropriate toolbar first. The tools required for georeferencing are not currently displayed in ArcMap. Select the Hollow box Make the Outline Color black and the Outline Width = 2. Click on the coloured box beneath GP_states_1930. Now you will “symbolize” (change the graphic representation) of the GP_states_1930 layer. Click on the Source tab and scroll down under the Data Source section to observe the layer’s coordinate system (USA_Contiguous_Albers_Equal_Area_Conic).  Double-click on GP_states_1930 to bring up its Layer Properties. The GP_states_1930 layer we just added is the reference layer and it MUST be added first because it provides the spatial reference or coordinate system for your unreferenced image. When referred to as “georectification”, the process entails that a new image is created when the original is “warped”, or rectified. This process is sometimes called “rubber-sheeting” because it treats the scanned historic map as a sort of rubber sheet that can be stretched and manipulated to fit real world features. Coordinates are tied to the image by identifying common geographic features also found in the reference dataset. These coordinates are obtained from a second dataset (raster or vector) that has a properly specified “spatial reference” (sometimes also referred to as “coordinate system”). Key Concept : Georeferencing is the process of assigning coordinates to an otherwise “ unreferenced” image. On the right side of your screen appears a corresponding map of the 12 Great Plains states as they existed in 1930. On the left side of your screen in the Table Of Contents (TOC) a new layer appears represented by a coloured box below it. Navigate to ArcGIS_Lesson3\WindErosion1.gdband select the feature class called GP_states_1930 then click the Add.
Double-click on GP_states_1930 to bring up its Layer Properties. The GP_states_1930 layer we just added is the reference layer and it MUST be added first because it provides the spatial reference or coordinate system for your unreferenced image. When referred to as “georectification”, the process entails that a new image is created when the original is “warped”, or rectified. This process is sometimes called “rubber-sheeting” because it treats the scanned historic map as a sort of rubber sheet that can be stretched and manipulated to fit real world features. Coordinates are tied to the image by identifying common geographic features also found in the reference dataset. These coordinates are obtained from a second dataset (raster or vector) that has a properly specified “spatial reference” (sometimes also referred to as “coordinate system”). Key Concept : Georeferencing is the process of assigning coordinates to an otherwise “ unreferenced” image. On the right side of your screen appears a corresponding map of the 12 Great Plains states as they existed in 1930. On the left side of your screen in the Table Of Contents (TOC) a new layer appears represented by a coloured box below it. Navigate to ArcGIS_Lesson3\WindErosion1.gdband select the feature class called GP_states_1930 then click the Add. 
If you unzipped the folder in Documents\ArcGIS you should be able to find it, but if you saved it elsewhere on your hard drive, you will need to use the Connect to Folder button.) (If you have trouble locating your folder, make sure you connected the ArcGIS_Lesson3 folder to ArcMap using the Connect to Folder button. Click File > Save (or Ctrl-S) and save to ArcGIS_Lesson3\ProjectFiles called mxd.From your computer desktop open the ArcMap.
ADD LAYER ARCMAP DOWNLOAD
Download the zipped file and save in your Documents\ArcGIS folder (remember to unzip the folder). National Archives, College Park, Maryland in the Soil Conservation Service documents found in RG 114, Entry 5, 330/c/17/2-1. The 1954 historical erosion map used in this exercise comes from the U.S. Features shown on a raster map can later be “vectorized” meaning converted to vector data. It is valuable because it allows researchers to conduct more detailed spatial analysis of the features in historic maps. One of the most valuable aspects to raster data is that it can be georeferenced. One of the imitations of raster data resides in its cell resolution (or pixel size) which doesn’t prove useful when we zoom in close. As an environmental historian the first step in many analytical processes using historical GIS is to convert raster data to vector data, a process that begins with georeferencing. Each point, line or polygon represents a feature on a map. The difference between the two is that vector data is made up of points, lines and polygons. There are two types of data in ArcGIS – vector and raster. 
ADD LAYER ARCMAP HOW TO
This lesson will teach you how to georeference a scanned historic map as raster data in ArcMap. By: Geoff Cunfer, revised by Louis-Jean Faucher Introduction








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
